-
Tel : +86-591-86397381
-
Email : sale@hosempower.com
-
Skype : +86-13205904365
Tel : +86-591-86397381
Email : sale@hosempower.com
Skype : +86-13205904365

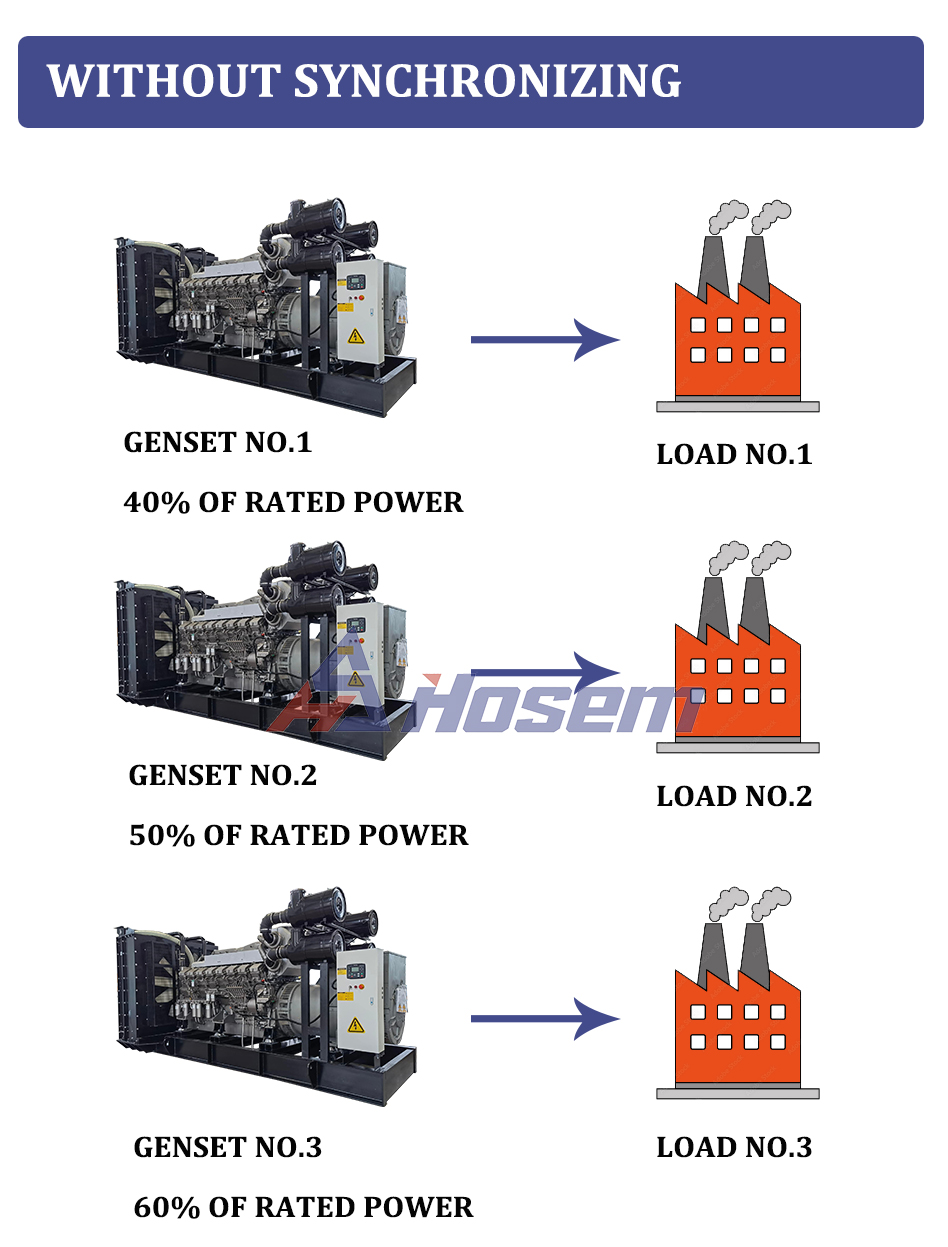
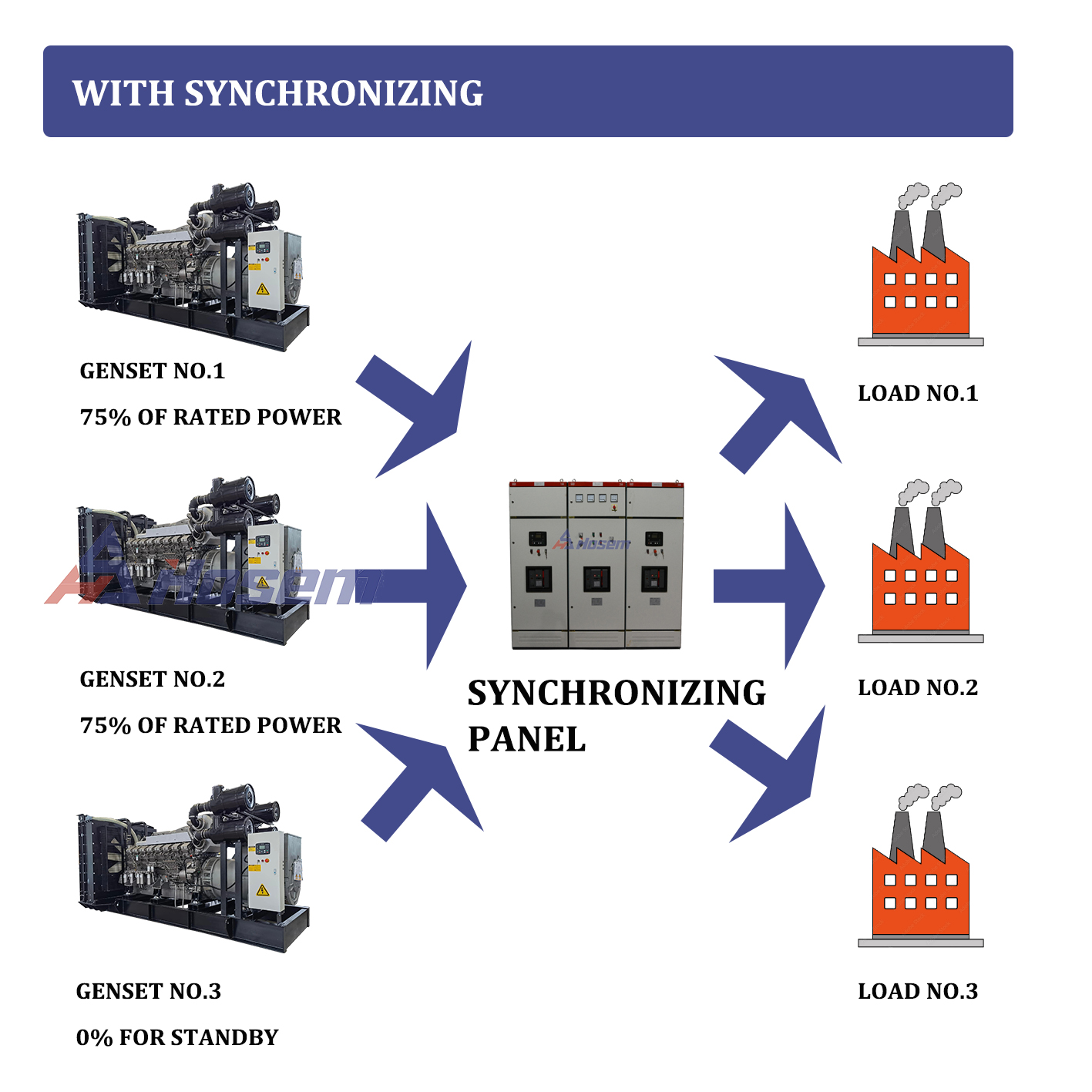
Paralleling in the context of electrical generators involves combining or synchronizing two power sources to generate a unified output voltage waveform. Essentially, it's the process of linking two generators, typically of similar brand, type, and size, to produce a combined wattage output that exceeds that of a single generator.
When these generators are connected in parallel, they operate in sync to enhance the overall power supply. This synchronized setup facilitates the provision of increased wattage, enabling the operation of more than just essential devices during power emergencies or to power larger systems or buildings.
Paralleling multiple power sources offers various advantages, providing increased reliability, flexibility in managing loads, and simplified maintenance with minimal disruptions. These parallel systems, where multiple generators are linked to a common bus, serve critical and emergency loads more effectively, especially in terms of response time and managing dynamic load shifts once in operation. The complexity of parallel standby systems comes with significant benefits in terms of reliability, redundancy, efficiency, expandability, and ease of maintenance.
**1. Redundancy:**
- *Enhanced Reliability:* Paralleling multiple generators increases reliability for critical loads. In case of a unit failure, backup loads can be redistributed among other generators, ensuring continuity. An N+1 configuration allows one generator to be offline for maintenance while still powering necessary loads, boosting reliability from 98% to 99.96%.
- *Elimination of Single Points of Failure:* Redundancy aims to eliminate single points of failure. Caution is needed to avoid moving failures to other system parts. Controls for redundancy must be carefully planned to prevent compromising reliability.
**2. Efficiency:**
- *Optimized Performance:* A parallel system operates more efficiently, reducing costs and losses. Larger generators may run at less than 30% capacity, causing inefficiencies. The ideal operational point is at 75-80% capacity for maximum efficiency, reducing fuel and maintenance costs.
- *Dynamic Load Control:* Paralleling systems can add or remove generators based on actual load demands, ensuring optimal performance and reducing fuel consumption.
**3. Expandability:**
- *Scalability and Modularity:* Parallel systems allow for scalability, accommodating fluctuations in power requirements. Additional generators can be seamlessly added as needed, offering flexibility in handling varying loads.
**4. Ease of Maintenance:**
- *Uninterrupted Service:* In an N+1 configuration, servicing or repairing one generator doesn't disrupt the function of other units. The redundancy inherent in a parallel system ensures a continuous power supply for critical circuits during maintenance or repair activities.
**Considerations for Implementation:**
- **Matching Generators:** Using generators from the same manufacturer, with similar ratings and type, is crucial to avoid load sharing issues and simplify maintenance and operations.
- **Standardization:** Standardizing on a single model type enhances maintenance and operational simplicity for the generator system. It also helps prevent load sharing issues between different generators in the system.
Implementing and maintaining a paralleling system requires careful planning, ensuring compatibility, and adherence to best practices to achieve optimal performance and reliability.